Product Description
Tped Empty CO2 Soda Aluminium Cylinder
Main Feature:
Model:AL06
Name: Soda CO2 cylinder
Material: seamless aluminium alloy
Gas type : CO2
Color: Silver
Type: Soda co2 tank
Water Capacity: 0.6L
Working Pressure: 150bar
Test Pressure: 225bar
Cylinders are made from high strength Aluminum Alloy 6061, reliable in durability, fracture toughness and resistance to tearing and cracking.
Highly corrosion-resistant interior and exterior-ideal for wet gases.
Cylinders perform well at low temperatures.
Lightweight--up to 40 percent lighter than comparable steel cylinders and in Consistent weight, consistent thickness resist damage.
Brushed external surface provides a low-maintenance finish.
Cylinders meet or exceed all regulatory standards worldwide.
Cylinders cycle-tested in excess of 120,000 cycles at service pressure. Excess of 12000 cycles at test pressure.
Minimum burst pressure tested to 2.5 times service pressure without failure.
* Valve & Threads can be specified & installed CHINAMFG Request.
* Standard Finishing is RAL300 Red Powder Coated.
* Markings according to Standard Specifications, Additional Markings Available Ipon Request.
certificate:
specification:
| Type | (mm) Outside Diameter |
(L) Water Capacity |
(mm) Height (Withoutvalve) |
(Kg) Weight(Without valve,cap) |
(Mpa) Working Pressure |
(mm) Design Wall Thickness |
| LW-60-0.5-20H | 60 | 0.5 | 285 | 0.6 | 200 | 3.1 |
| LW-75-0.7-15H | 75 | 0.7 | 295 | 0.9 | 150 | 4 |
| LW-82-0.7-15H | 82 | 0.7 | 235 | 0.9 | 150 | 4.2 |
| LW-89-1.0-15H | 89 | 1.0 | 269 | 1.2 | 150 | 4.5 |
| LW-89-1.4-15H | 89 | 1.4 | 345 | 1.4 | 150 | 4.5 |
| LW-108-1.0-15H | 108 | 1.0 | 210 | 1.3 | 150 | 5.5 |
| LW-108-1.4-15H | 108 | 1.4 | 264 | 1.6 | 150 | 5.5 |
| LW-108-2.0-15H | 108 | 2.0 | 346 | 2.1 | 150 | 5.5 |
| LW-108-2.5-15H | 108 | 2.5 | 413 | 2.5 | 150 | 5.5 |
| LW-120-2.0-15H | 120 | 2.0 | 320 | 2.7 | 150 | 6.1 |
| LW-120-2.5-15H | 120 | 2.5 | 369 | 3.0 | 150 | 6.1 |
| LW-120-2.8-15H | 120 | 2.8 | 398 | 3.2 | 150 | 6.1 |
| LW-120-3.2-15H | 120 | 3.2 | 437 | 3.5 | 150 | 6.1 |
| LW-140-4.0-15H | 140 | 4.0 | 420 | 4.2 | 150 | 7.1 |
| LW-140-5.0-15H | 140 | 5.0 | 500 | 4.9 | 150 | 7.1 |
| LW-140-6.0-15H | 140 | 6.0 | 580 | 5.6 | 150 | 7.1 |
| LW-140-8.0-15H | 140 | 8.0 | 741 | 7.2 | 150 | 7.1 |
| LW-140-5.0-20H | 140 | 5.0 | 525 | 6.3 | 200 | 9.3 |
| LW-140-6.0-20H | 140 | 6.0 | 652 | 7.98 | 200 | 9.3 |
| LW-159-10.0-15H | 159 | 10.0 | 730 | 8.8 | 150 | 8 |
| LW-184-9.0-20H | 184 | 9.0 | 575 | 12.0 | 200 | 12.2 |
| LW-184-10.0-20H | 184 | 10.0 | 620 | 12.9 | 200 | 12.2 |
| LW-184-11.0-20H | 184 | 11.0 | 665 | 14.2 | 200 | 12.2 |
| LW-184-12.0-20H | 184 | 12.0 | 710 | 15.4 | 200 | 12.2 |
| LW-203-12-15H | 203 | 12.0 | 567 | 11.8 | 150 | 10.3 |
| LW-203-15-15H | 203 | 20.0 | 873 | 17.0 | 150 | 10.3 |
| LW-203-21.3-15H | 203 | 21.3 | 962 | 19.9 | 150 | 10.3 |
| LW-204-12-20H | 204 | 12.0 | 610 | 16.5 | 200 | 13.4 |
| LW-204-15-20H | 204 | 15.0 | 735 | 18.7 | 200 | 13.4 |
| LW-204-20-20H | 204 | 20.0 | 940 | 23.4 | 200 | 13.4 |
| LW-232-29.5-15H | 232 | 29.5 | 994 | 30.2 | 150 | 11.7 |
| LW-232-30.3-15H | 232 | 30.0 | 1571 | 30.5 | 150 | 11.7 |
| LW-232-33.4-15H | 232 | 33.4 | 1126 | 31.3 | 150 | 11.7 |
| LW-232-40.0-15H | 232 | 40.0 | 1340 | 36.5 | 150 | 11.7 |
| LW-232-20.0-20H | 232 | 20.0 | 750 | 26.9 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-232-26.0-20H | 232 | 26.0 | 921 | 30.7 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-232-30.0-20H | 232 | 30.0 | 1076 | 36.4 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-232-31.5-20H | 232 | 31.5 | 1096 | 38.0 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-232-40.0-20H | 232 | 40.0 | 1365 | 44.1 | 200 | 15.4 |
| LW-250-40.0-15H | 250 | 40.0 | 1150 | 36.7 | 150 | 12.6 |
| LW-250-46.4-15H | 250 | 46.4 | 1305 | 38.7 | 150 | 12.6 |
| LW-250-47.5-15H | 250 | 47.5 | 1340 | 42.0 | 150 | 12.6 |
| LW-250-50.0-15H | 250 | 50.0 | 1590 | 39.0 | 200 | 12.6 |
| LW-250-40.0-20H | 250 | 40.0 | 1227 | 46.3 | 200 | 16.5 |
| LW-250-50.0-20H | 250 | 50.0 | 1500 | 56.0 | 200 | 16. |
Company profile:
Our factory aluminium jar-making co.,ltd. is a professional filter capacitor shell aluminum shell and the development and production of a wholly-owned enterprise. Founded in 1988, now covers an area of 80,000 square meters, staff 320 people, including engineers and technicians 25 people. Since its inception, that is fully committed to the manufacture of aluminum cans , aluminum semi-finished products processing and metallurgy and processing such as special-shaped parts, with a strong technical force and good quality staff, and constantly develop new products, develop new markets,
Growing scale of production. Products not only meet the domestic demand, but also exported to Europe, America and Southeast Asia regions, well received by customers and vendors praise!
Company's existing 3 series of products, Capacitor aluminum shell and cover, fuel filter housing and shelters, EFI pump casing. The company pays great attention to product quality, strictly follow the concept of lean production and methods of management of production. And has achieved ISO9001:2008quality system.certification.ISO14001:2004, EN ISO7866:2012+AC2014 environmental management system certification and ISO/TS16949: 2009auto parts industry certification.
The company in line to provide customers with the fastest, most comprehensive and efficient services for the purpose, sincerely welcome friends home and abroad to write to.
| Function: | Storage Pressure Vessel, Cream Charger |
|---|---|
| Application: | Gas |
| Material: | Aluminum Alloy |
| Pressure: | 10.0MPa≤p<100.0MPa |
| Storage Medium: | Food Grade CO2 |
| Pressure Level: | High Pressure (10.0MPa≤p<100.0MPa) |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
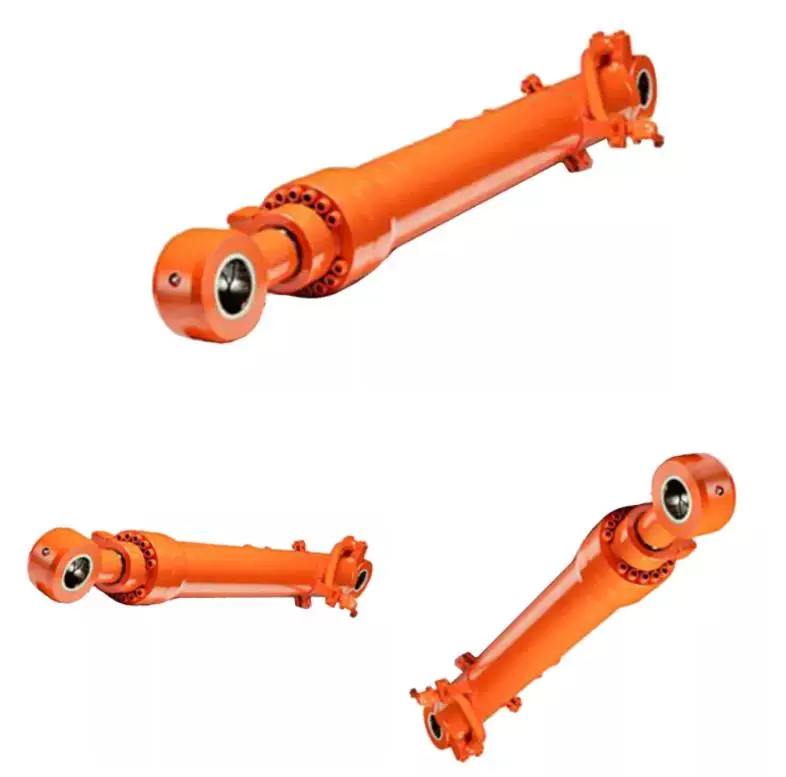

How do hydraulic cylinders handle the challenges of minimizing friction and wear?
Hydraulic cylinders employ several mechanisms and techniques to effectively minimize friction and wear, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Minimizing friction and wear is crucial for hydraulic cylinders as it helps to maintain efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and prevent premature failure. Here's a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders handle the challenges of minimizing friction and wear:
1. Lubrication:
- Proper lubrication is essential for minimizing friction and wear in hydraulic cylinders. Lubricating fluids, such as hydraulic oils, are used to create a thin film between moving surfaces, reducing direct metal-to-metal contact. This lubricating film acts as a protective barrier, reducing friction and preventing wear. Regular maintenance practices include monitoring and maintaining the appropriate lubricant levels to ensure optimal lubrication and minimize frictional losses.
2. Surface Finishes:
- The surface finishes of components in hydraulic cylinders play a crucial role in minimizing friction and wear. Smoother surface finishes, achieved through precision machining, grinding, or the application of specialized coatings, reduce surface roughness and frictional resistance. By minimizing surface irregularities, the risk of wear and friction-induced damage is significantly reduced, resulting in improved efficiency and extended component life.
3. High-Quality Sealing Systems:
- Well-designed and high-quality sealing systems are crucial for minimizing friction and wear in hydraulic cylinders. Seals prevent fluid leakage and contamination while maintaining proper lubrication. Advanced sealing materials, such as polyurethane or composite materials, offer excellent wear resistance and low friction characteristics. Optimal seal design and proper installation ensure effective sealing, minimizing friction and wear between the piston and cylinder bore.
4. Proper Alignment and Clearances:
- Hydraulic cylinders must be properly aligned and have appropriate clearances to minimize friction and wear. Misalignment or excessive clearances can result in increased friction and uneven wear, leading to premature failure. Proper installation, alignment, and maintenance practices, including regular inspection and adjustment of clearances, help ensure smooth and even movement of the piston within the cylinder, reducing friction and wear.
5. Filtration and Contamination Control:
- Effective filtration and contamination control are essential for minimizing friction and wear in hydraulic cylinders. Contaminants, such as particles or moisture, can act as abrasive agents, accelerating wear and increasing friction. By implementing robust filtration systems and proper maintenance practices, hydraulic systems can prevent the ingress of contaminants, ensuring clean and properly lubricated components. Clean hydraulic fluids help minimize wear and friction, contributing to improved performance and longevity.
6. Material Selection:
- The selection of appropriate materials for hydraulic cylinder components is crucial in minimizing friction and wear. Components subject to high frictional forces, such as pistons and cylinder bores, can be made from materials with excellent wear resistance, such as hardened steel or composite materials. Additionally, selecting materials with low coefficients of friction helps reduce frictional losses. Proper material selection ensures durability and minimized wear in critical components of hydraulic cylinders.
7. Maintenance and Regular Inspection:
- Regular maintenance and inspection practices are vital for identifying and addressing potential issues that could lead to increased friction and wear in hydraulic cylinders. Scheduled maintenance includes lubrication checks, seal inspections, and monitoring of clearances. By promptly detecting and rectifying any signs of wear or misalignment, hydraulic cylinders can be kept in optimal condition, minimizing friction and wear throughout their operational lifespan.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders employ various strategies to handle the challenges of minimizing friction and wear. These include proper lubrication, employing suitable surface finishes, utilizing high-quality sealing systems, ensuring proper alignment and clearances, implementing effective filtration and contamination control measures, selecting appropriate materials, and conducting regular maintenance and inspections. By implementing these practices, hydraulic cylinders can minimize friction and wear, ensuring smooth and efficient operation while extending the overall lifespan of the system.

Handling the Challenges of Minimizing Fluid Leaks and Contamination in Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders face challenges when it comes to minimizing fluid leaks and contamination, as these issues can impact the performance, reliability, and lifespan of the system. However, there are several measures and design considerations that help address these challenges effectively. Let's explore how hydraulic cylinders handle the challenges of minimizing fluid leaks and contamination:
- Sealing Systems: Hydraulic cylinders employ advanced sealing systems to prevent fluid leaks. These systems typically include various types of seals, such as piston seals, rod seals, and wiper seals. The seals are designed to create a tight and reliable barrier between the moving components of the cylinder and the external environment, minimizing the risk of fluid leakage.
- Seal Material Selection: The choice of seal materials is crucial in minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. Hydraulic cylinder manufacturers carefully select seal materials that are compatible with the hydraulic fluid used and resistant to wear, abrasion, and chemical degradation. This ensures the longevity and effectiveness of the seals, reducing the likelihood of leaks or premature seal failure.
- Proper Installation and Maintenance: Ensuring proper installation and regular maintenance of hydraulic cylinders is essential for minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. During installation, attention should be given to proper alignment, torqueing of bolts, and adherence to recommended procedures. Regular maintenance includes inspecting seals, replacing worn-out components, and addressing any signs of leakage promptly. Proper maintenance practices help identify and rectify issues before they escalate and cause significant problems.
- Contamination Control: Hydraulic cylinders incorporate measures to control contamination and maintain fluid cleanliness. This includes the use of filtration systems, such as in-line filters, to remove particles and contaminants from the hydraulic fluid. Additionally, hydraulic reservoirs often have breathers and desiccant filters to prevent moisture and airborne contaminants from entering the system. By controlling contamination, hydraulic cylinders minimize the risk of damage to internal components and maintain optimal system performance.
- Environmental Protection: Hydraulic cylinders may be equipped with protective features to safeguard against external contaminants. For example, bellows or protective boots can be installed to shield the rod and seals from debris, dirt, or moisture present in the operating environment. These protective measures help extend the life of the seals and enhance the overall reliability of the hydraulic cylinder.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders employ sealing systems, appropriate seal materials, proper installation and maintenance practices, contamination control measures, and environmental protection features to handle the challenges of minimizing fluid leaks and contamination. By implementing these measures, manufacturers can ensure reliable and long-lasting hydraulic cylinder performance, minimize the risk of fluid leakage, and maintain the cleanliness of the hydraulic system.
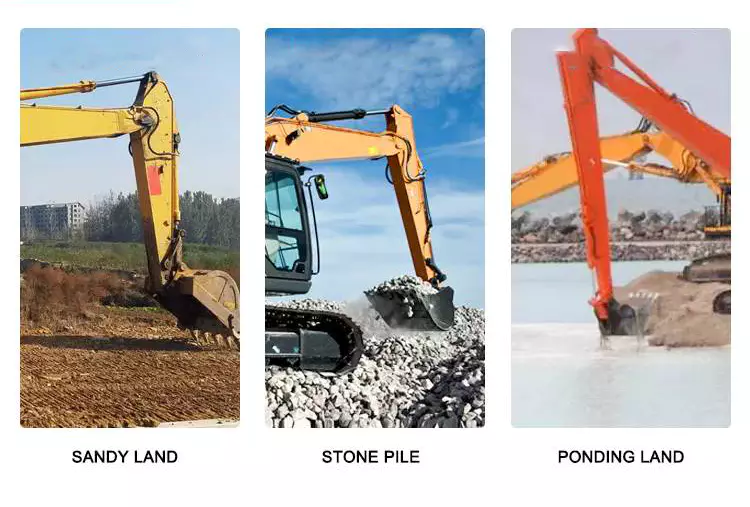

How do hydraulic cylinders generate force and motion using hydraulic fluid?
Hydraulic cylinders generate force and motion by utilizing the principles of fluid mechanics, specifically Pascal's law, in conjunction with the properties of hydraulic fluid. The process involves the conversion of hydraulic energy into mechanical force and linear motion. Here's a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders achieve this:
1. Pascal's Law:
- Hydraulic cylinders operate based on Pascal's law, which states that when pressure is applied to a fluid in a confined space, it is transmitted equally in all directions. In the context of hydraulic cylinders, this means that when hydraulic fluid is pressurized, the force is evenly distributed throughout the fluid and transmitted to all surfaces in contact with the fluid.
2. Hydraulic Fluid and Pressure:
- Hydraulic systems use a specialized fluid, typically hydraulic oil, as the working medium. This fluid is stored in a reservoir and circulated through the system by a hydraulic pump. The pump pressurizes the fluid, creating hydraulic pressure that can be controlled and directed to various components, including hydraulic cylinders.
3. Cylinder Design and Components:
- Hydraulic cylinders consist of several key components, including a cylindrical barrel, a piston, a piston rod, and various seals. The barrel is a hollow tube that houses the piston and allows for fluid flow. The piston divides the cylinder into two chambers: the rod side and the cap side. The piston rod extends from the piston and provides a connection point for external loads. Seals are used to prevent fluid leakage and maintain hydraulic pressure within the cylinder.
4. Fluid Input and Motion:
- To generate force and motion, hydraulic fluid is directed into one side of the cylinder, creating pressure on the corresponding surface of the piston. This pressure is transmitted through the fluid to the other side of the piston.
5. Force Generation:
- The force generated by a hydraulic cylinder is a result of the pressure applied to a specific surface area of the piston. The force exerted by the hydraulic cylinder can be calculated using the formula: Force = Pressure × Area. The area is determined by the diameter of the piston or the piston rod, depending on which side of the cylinder the fluid is acting upon.
6. Linear Motion:
- As the pressurized hydraulic fluid acts on the piston, it generates a force that moves the piston in a linear direction within the cylinder. This linear motion is transferred to the piston rod, which extends or retracts accordingly. The piston rod can be connected to external components or machinery, allowing the generated force to perform various tasks, such as lifting, pushing, pulling, or controlling mechanisms.
7. Control and Regulation:
- The force and motion generated by hydraulic cylinders can be controlled and regulated by adjusting the flow of hydraulic fluid into the cylinder. By regulating the flow rate, pressure, and direction of the fluid, the speed, force, and direction of the cylinder's movement can be precisely controlled. This control allows for accurate positioning, smooth operation, and synchronization of multiple cylinders in complex machinery.
8. Return and Recirculation of Fluid:
- After the hydraulic cylinder completes its stroke, the hydraulic fluid on the opposite side of the piston needs to be returned to the reservoir. This is typically achieved through hydraulic valves that control the flow direction, allowing the fluid to return and be recirculated in the system for further use.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders generate force and motion by utilizing the principles of Pascal's law. Pressurized hydraulic fluid acts on the piston, creating force that moves the piston in a linear direction. This linear motion is transferred to the piston rod, allowing the generated force to perform various tasks. By controlling the flow of hydraulic fluid, the force and motion of hydraulic cylinders can be precisely regulated, contributing to their versatility and wide range of applications in machinery.

editor by CX 2023-11-28