Product Description
Guaranteed Quality Double Action Mobile Crane Hydraulic Steering Cylinder price for sale
Hydraulic Steering Cylinder for Mobile Cranes
A mobile crane steering cylinder is a hydraulic component that is part of the steering system of a mobile crane. It plays a crucial role in allowing the operator to control the direction of the crane by actuating the steering mechanism.
Here's how the mobile crane steering cylinder works:
-
Hydraulic Power: A hydraulic system typically powers The mobile crane steering system. The steering cylinder receives pressurized hydraulic fluid from the crane's hydraulic pump.
-
Cylinder Design: The steering cylinder consists of a cylindrical barrel with a piston and rod assembly inside. The cylinder is usually double-acting, which can exert force in both directions.
-
Mounting and Connection: The steering cylinder is mounted CHINAMFG the crane's chassis or steering mechanism. It is connected to other steering system components, such as the steering linkage, tie rod, or steering gear.
-
Steering Input: When the operator turns the steering wheel or control lever in the crane's cabin, it activates the steering control valve. The control valve regulates the flow of hydraulic fluid to the steering cylinder.
-
Hydraulic Fluid Flow: Depending on the desired steering direction, the control valve directs the pressurized hydraulic fluid to the port on 1 side or the other side of the steering cylinder.
-
Cylinder Actuation: The pressurized hydraulic fluid enters the appropriate port of the steering cylinder, creating pressure against the piston inside. This pressure causes the piston to move, pushing or pulling the rod connected to it.
-
Steering Mechanism: The movement of the steering cylinder's rod translates into the action of other connected components in the steering system. This movement, in turn, causes the crane's wheels or axles to turn, enabling steering in the desired direction.
-
Steering Control: The operator can control the extent and speed of the steering by adjusting the input from the steering wheel or control lever. The hydraulic fluid flow to the steering cylinder can be regulated to provide precise steering control.
How is the steering cylinder connected to the steering linkage and steering gear?
-
The steering cylinder of a mobile crane is connected to the steering linkage and steering gear to facilitate the transfer of hydraulic force and motion for steering control. Here's how the steering cylinder is typically connected:
-
Steering Linkage: The steering linkage consists of various mechanical components, such as tie rods, drag links, and pitman arms, that transmit the motion from the steering cylinder to the wheels or axles of the crane.
-
Cylinder Mounting: The steering cylinder is mounted CHINAMFG the crane's chassis or steering mechanism using brackets or mounting points. It is securely attached to ensure stability and proper alignment.
-
Rod Connection: The rod end of the steering cylinder is connected to the steering linkage. This connection is typically achieved using a ball joint or a clevis joint. The ball joint allows for angular movement, accommodating the varying angles and forces during steering.
-
Steering Gear: The other end of the steering linkage is connected to the steering gear, sometimes called the steering box or rack. The steering gear is responsible for converting the rotational motion provided by the steering cylinder into linear motion for the wheels or axles.
-
Tie Rods: The tie rods are an essential part of the steering linkage that connects the steering gear to the steering knuckles or wheel spindles of the crane. The tie rods transmit the force and motion from the steering gear to steer the wheels in the desired direction.
-
Steering Knuckles: The steering knuckles are located at the ends of the axles or wheel spindles. They are connected to the tie rods and accommodate the movement of the wheels as directed by the steering cylinder and steering linkage.
Our Company
We have a first-class independent R&D platform for assembly. The forklift cylinder production workshop has 4 semi-automatic lifting cylinder assembly lines and 1 fully automatic tilting cylinder assembly line, with a designed annual production capacity of 1 million pieces; the special cylinder workshop is equipped with semi-automatic cleaning and assembly systems of various specifications, with a designed annual production capacity of 200,000 essays. It has famous CNC machining equipment, machining centers, special equipment for high-precision cylinder processing, robot welding machines, automatic cleaning machines, automatic cylinder assembly machines, and automatic paint production lines. We have more than 300 sets of critical equipment running. The optimized allocation and efficient utilization of equipment resources ensure the precision requirements of the products and meet the high standard quality requirements of the products.
|
Forklift cylinder assembly shop |
Other types of cylinder assembly shop |
Welding
Painting & coating
|
Painting & coating line |
Fully automatic water-based |
Testing
To further improve product performance, and establish the leadership position of our hydraulic cylinder in the industry, our company and zjimee jointly established a Comprehensive performance laboratory of hydraulic cylinders, hydraulic valves, and hydraulic pumps; the lab is computer-assisted testing, using electro-hydraulic control technology, the test conditions preset by computer, which improves the test accuracy and system versatility, and the experimental data.
The automatic collection is realized through the application of sensors, and the output data, such as the internal leakage and load efficiency of the cylinder or the valve, are directly processed by the computer and converted to standard units (ml/min; %). At the same time, to ensure the working safety of the hydraulic system, the state monitoring function is carried out for key performance parameters, such as "oil temperature monitoring, liquid level monitoring, filter device monitoring," etc. Among them, the hydraulic cylinder test stand can test the performance of "load efficiency" and "internal leakage" by readings. At the same time, it is equipped with a grating ruler measuring instrument, which meets the requirements of all test items of hydraulic cylinder products in the national standard.
Our Factory
Packaging & Shipping
| Certification: | GS, RoHS, CE, ISO9001 |
|---|---|
| Pressure: | High Pressure |
| Work Temperature: | Normal Temperature |
| Acting Way: | Double Acting |
| Working Method: | Rotary |
| Adjusted Form: | Regulated Type |
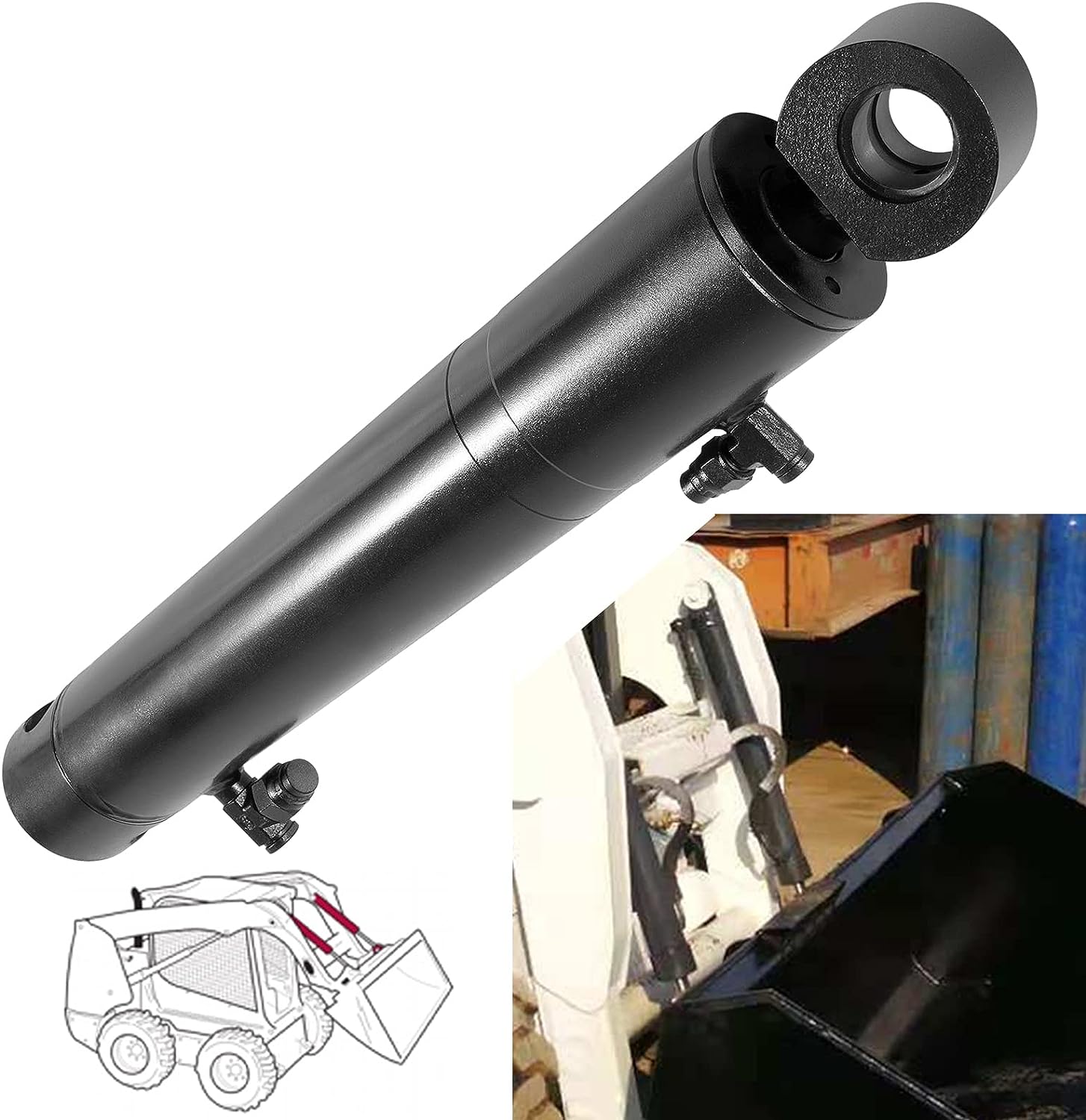

How does a tilt cylinder handle variations in hydraulic pressure and flow rate?
A tilt cylinder is designed to handle variations in hydraulic pressure and flow rate effectively. It incorporates specific features and mechanisms that allow it to operate reliably under different hydraulic conditions. Here's a detailed explanation:
- Pressure Compensation: Tilt cylinders are equipped with pressure compensation mechanisms to handle variations in hydraulic pressure. These mechanisms ensure that the cylinder can function properly even when the hydraulic system experiences fluctuations in pressure. The pressure compensation feature allows the cylinder to maintain consistent force and performance, regardless of the changes in hydraulic pressure.
- Flow Control: Tilt cylinders are designed to accommodate variations in hydraulic flow rate. They have internal passages and ports that allow the hydraulic fluid to flow into and out of the cylinder. The cylinder's design ensures that it can handle different flow rates without compromising its functionality. Whether the hydraulic flow rate is high or low, the tilt cylinder can adjust accordingly and provide the necessary force and control for load manipulation.
- Sealing Mechanisms: Tilt cylinders incorporate sealing mechanisms to prevent leakage and maintain hydraulic integrity. These seals are designed to withstand variations in pressure and flow rate, ensuring that the hydraulic fluid remains contained within the cylinder. The seals also help maintain the required pressure within the cylinder, allowing it to operate efficiently and effectively, regardless of the hydraulic conditions.
- Internal Design: The internal design of a tilt cylinder takes into account variations in hydraulic pressure and flow rate. The cylinder's internal components, such as piston, rod, and cylinder barrel, are engineered to withstand different hydraulic conditions. They are designed to handle the forces exerted by varying pressure and flow rates, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the cylinder.
- Hydraulic System Compatibility: Tilt cylinders are designed to be compatible with the hydraulic systems of the equipment they are installed in. Manufacturers ensure that the cylinders can handle the expected pressure and flow rate ranges of the hydraulic system. This compatibility allows for seamless integration and optimal performance, even when there are variations in hydraulic conditions.
- Quality Control and Testing: Tilt cylinders undergo rigorous quality control measures and testing during the manufacturing process. These measures ensure that the cylinders can handle variations in hydraulic pressure and flow rate within specified tolerances. Manufacturers test the cylinders under different hydraulic conditions to verify their performance, reliability, and ability to handle variations in pressure and flow.
By incorporating pressure compensation mechanisms, flow control features, sealing mechanisms, robust internal design, hydraulic system compatibility, and thorough quality control, tilt cylinders are capable of handling variations in hydraulic pressure and flow rate. These cylinders provide reliable and consistent performance, regardless of the hydraulic conditions, ensuring smooth and efficient operation in material handling and construction equipment.
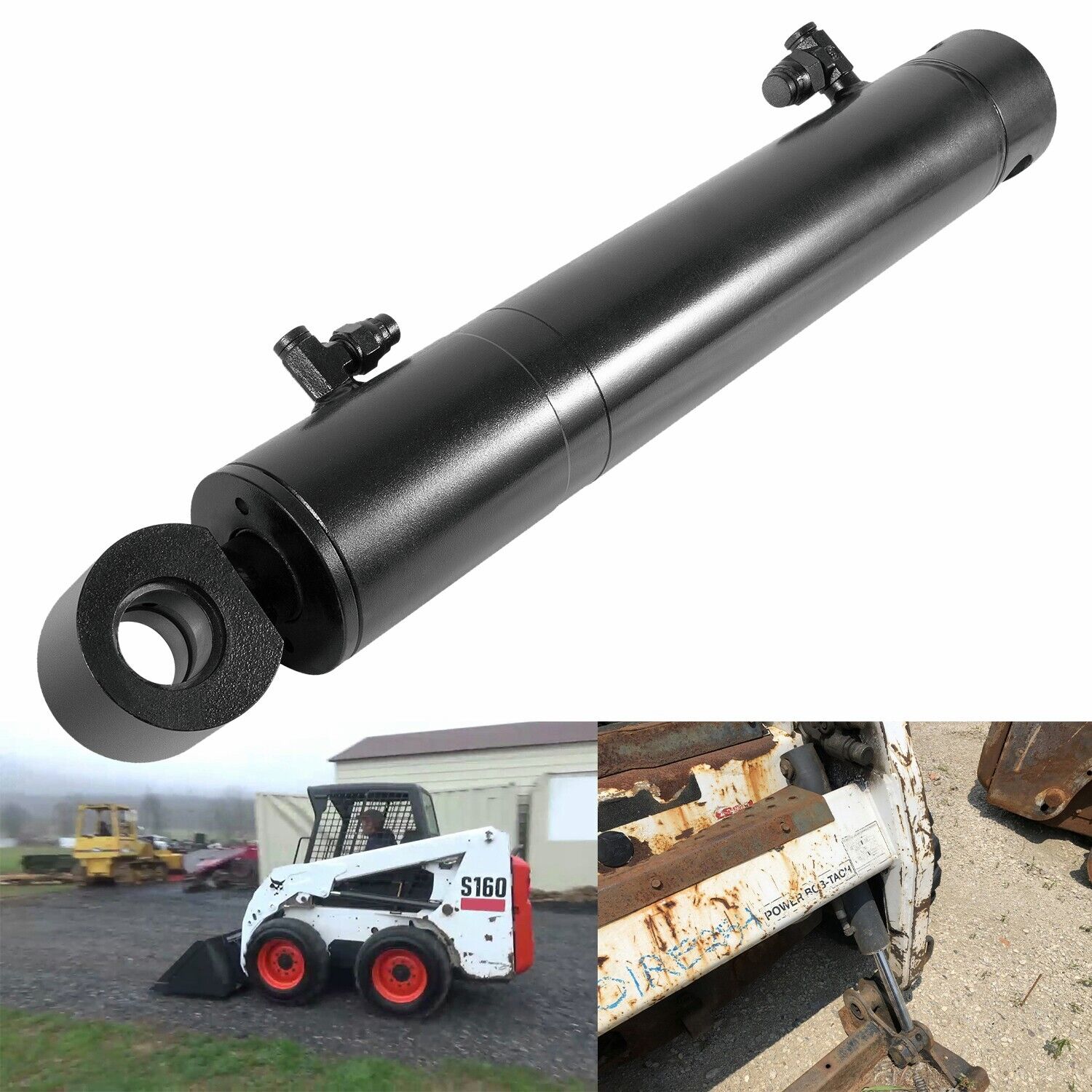

What are the safety considerations when using machinery equipped with tilt cylinders?
When using machinery equipped with tilt cylinders, several safety considerations should be taken into account to ensure the well-being of operators, bystanders, and the overall work environment. Here are the key safety considerations:
- Operator Training: Proper training is essential for operators who will be working with machinery equipped with tilt cylinders. Operators should receive comprehensive training on the safe operation of the equipment, including understanding the controls, precautions, and potential hazards associated with tilt cylinder usage. Training helps operators develop the necessary skills and knowledge to operate the machinery safely.
- Safe Operating Procedures: Establishing and following safe operating procedures is crucial for minimizing risks when using machinery with tilt cylinders. Standard operating procedures should outline the correct sequence of operations, safety checks, and precautions to be taken before, during, and after using the equipment. Operators should adhere to these procedures to ensure safe and consistent operation.
- Inspection and Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of the tilt cylinders and associated equipment components are essential for safety. This includes checking for leaks, damage, loose connections, or excessive wear. Any identified issues should be promptly addressed through maintenance or repairs to prevent potential malfunctions or accidents during operation.
- Load Capacity and Stability: Tilt cylinders have specific load capacity limits, and exceeding these limits can compromise safety. Operators should be aware of the equipment's load capacity and ensure that the loads being lifted or tilted fall within the specified limits. Additionally, attention should be given to maintaining the stability of the machinery during tilting operations, considering factors such as uneven terrain or shifting loads.
- Proper Use of Safety Devices: Machinery equipped with tilt cylinders may have additional safety devices such as safety locks, sensors, or audible alarms. Operators should use these safety devices as intended and ensure they are in good working condition. For example, safety locks should be engaged when the equipment is stationary to prevent unintended tilting.
- Clear Communication and Signaling: Clear communication among operators, signalers, and other personnel is vital for ensuring safety during tilt cylinder operations. Hand signals or radio communication should be used effectively to convey instructions and warnings. Adequate signaling and communication protocols should be established and followed to avoid misunderstandings or accidents.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators and personnel working with machinery equipped with tilt cylinders should wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including safety helmets, protective eyewear, gloves, and high-visibility clothing. PPE helps minimize the risk of injury from potential hazards, such as falling objects, debris, or hydraulic fluid leaks.
By considering these safety aspects and implementing appropriate measures, the risks associated with using machinery equipped with tilt cylinders can be mitigated. Prioritizing safety promotes a secure working environment, reduces accidents, and protects the well-being of everyone involved in the operation.

How does a tilt cylinder differ from other types of hydraulic cylinders?
A tilt cylinder has specific characteristics and functionalities that differentiate it from other types of hydraulic cylinders. While hydraulic cylinders serve various purposes in different applications, here are the key ways in which a tilt cylinder differs:
- Tilting Functionality: The primary distinction of a tilt cylinder is its ability to provide controlled tilting or angling of components. Unlike other hydraulic cylinders that primarily focus on linear motion, a tilt cylinder is specifically designed to enable angular movement. It allows for the adjustment of the working angle of attachments, such as buckets or blades, in heavy machinery.
- Mounting Orientation: Tilt cylinders are typically mounted in a horizontal or near-horizontal orientation, allowing for effective tilting movement. In contrast, other hydraulic cylinders may be mounted vertically, horizontally, or at various angles depending on their specific application requirements.
- Range of Motion: While other hydraulic cylinders may have a limited range of motion, typically in the form of extending or retracting the piston rod, a tilt cylinder offers a broader range of motion. It allows for continuous and controlled tilting action within a specific angular range, providing flexibility and adaptability in heavy machinery operations.
- Control Mechanisms: Tilt cylinders often require specialized control mechanisms to regulate the tilting movement accurately. Hydraulic systems controlling tilt cylinders incorporate valves, pressure regulators, and other components specifically designed for precise control of the angular motion. In contrast, other hydraulic cylinders may utilize different control mechanisms tailored to their particular linear motion requirements.
- Application-Specific Design: Tilt cylinders are engineered to meet the specific demands of heavy machinery applications that involve tilting or angling of components. They are designed to withstand high loads, provide precise control, and ensure reliable performance in challenging work environments. Other types of hydraulic cylinders, such as single-acting, double-acting, telescopic, or differential cylinders, are designed for different purposes and may have distinct structural and functional features.
While tilt cylinders share the fundamental principles of hydraulic cylinders, their specialization in tilting functionality sets them apart from other types of hydraulic cylinders. The unique design, mounting orientation, range of motion, control mechanisms, and application-specific characteristics make tilt cylinders suitable for tasks that require controlled angular movement in heavy machinery applications.
In conclusion, a tilt cylinder differs from other types of hydraulic cylinders through its dedicated focus on providing controlled tilting functionality, specialized design, and specific mounting orientation. These distinctions enable tilt cylinders to fulfill the unique requirements of heavy machinery applications involving angular adjustments and enhance the versatility and performance of the equipment.

editor by CX 2023-12-02